A general tutorial on installing Arduino bootloader on ATmega8 AVR microcontroller and programming it using Arduino IDE.
- 71,875 views
- 26 comments
- 24 respects
AVR controller contains single or multiple UART PORT. A UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) is the microchip with programming that controls a Controller’s interface to its attached serial devices. Look at this article for more information about UART. Here we’ll learn AVR ATmega8 UART. ATmega8 has single UART port. Hello everyone, I am learning how to use header files with UART on ATmega8. I have two problems: First one for some reason the registers like identifier “UBRR0L” is undefined and the rest of them. And the second one is it does not include the header file. I dont know if these two problem are related. I have tried my best to resolve using examples but to no end. Here are the screenshots. In this case, the code may work correctly, since UBRRH defaults to a value of zero at power up. But, it will work for the wrong reason. You'll be better off initializing UCSRC using direct assignement rather than a R-M-W construct Or, you could choose to skip initialization of UCSRC altogether - the values you OR'ed in the first place are totally compatible with UCSRC's power-on default.
Components and supplies
| × | 1 | |
| × | 1 | |
| × | 1 | |
| × | 1 | |
| × | 2 | |
| × | 1 | |
| × | 1 | |
| × | 1 | |
| × | 12 | |
| × | 4 |
About this project
“I’ve written my code for Arduino UNO board. Is it possible to upload my sketch to an AVR microcontroller except ATmega328? I think it’s the most common question of Arduino lovers. This may have different reasons such as:
- Using a cheaper AVR microcontroller
- Require an AVR microcontroller with more or even less pins than ATmega328
- You have all kinds of AVR except ATmega328 :D
In this tutorial you will learn how to program an ATmega8 using Arduino IDE. It’s not restricted to ATmega8 only and can be generalized to other cores which are available at MCUDude’s GitHub. It consists of two parts. In part one, Installing Arduino bootloader on ATmega8 is described. Part two shows how to program an ATmega8 using Arduino IDE and a USB to TTL convertor.
Part one: Installing Arduino Bootloader
In this part, we add ATmega8 support to Arduino IDE. Then we set up the breadboard and connect ATmega8 to Arduino UNO board.
Step One: Adding ATmega8 Support to Arduino IDE Using Board Manager
There are different types of cores available on MCUDude’s GitHub repository. MiniCore is used for ATmega8 microcontroller. Supported microcontrollers in this core are:
- ATmega8
- ATmega48
- ATmega88
- ATmega168
- ATmega328
Follow steps below to install MiniCore in your Arduino IDE.
- In File menu, click on Preferences.
- Now in Additional Boards Manger URLs, enter the following URL:
- Go to Tools menu and then select Board > Boards Manager
- In Boards Manager window, search for MiniCore and then install the latest version.
The above steps are shown graphically here:
ATmega8 pinout is shown in the following figure.
Step Two: Programming Arduino as an ISP (In-system programming)
To burn Arduino bootloader, we need to make our Arduino UNO as an ISP. There’s a sketch named ArduinoISP in the built-in examples of Arduino IDE. Follow these steps to program your Arduino UNO as an ISP.
- Open File > Examples > 11.ArduinoISP > ArduinoISP
- Upload this sketch to your Arduino UNO.
Step Three: Burning Bootloader
- Connect Arduino to ATmega8 as below.
Arduino ----------ATmega8
SCK / Pin 13 ----------SCK / PB5
MISO / Pin 12 ----------MISO / PB4
MOSI / Pin 11 ----------MOSI / PB3
SSN / Pin 10 ----------RESET
- Go to Tools > Board and select ATmega8. You can also select your clock type and frequency in Tools menu.
- Select programmer type in Tools > Programmer: as “Arduinoas ISP”.
- Now in Tools menu, click on the Burn Bootloader.
If the operation was successful, it says “Done burning bootloader”. Congratulations! You have done it.
Part Two: Programming ATmega8 Using Arduino IDE and a USB to TTL Convertor

Here we have an ATmega8 with Arduino bootloader. As you know, there is a USB to TTL convertor on all Arduino boards. It acts as a bridge between microcontroller and Arduino IDE. We use CH340 USB to TTL convertor module to upload the sketch to ATmega8.
Step Four: Setting up the Connections
Connect components as shown below.
CH340 ---------- ATmega8
VCC ---------- VCC
GND ---------- GND
Tx ---------- RX / PD0
Rx ---------- Tx / PD1
Step Five: Uploading the Sketch to ATmega8
Press and hold the reset pushbutton. Now click on upload in IDE. Hold the pushbutton until it says “Uploading…”on the IDE status bar. Release the button after uploading process begins. It’s because microcontroller should be in the RESET state when the uploading process starts.
Note: If the process was unsuccessful, place a 100nF capacitor at Vcc and GND of microcontroller as close as possible.
Note: Some USB to TTL convertor modules have a pin named DTR. If yours has this pin too, you can connect it to the RESET pin of ATmega8 and there’s no need to use the pushbutton to manually reset the microcontroller.
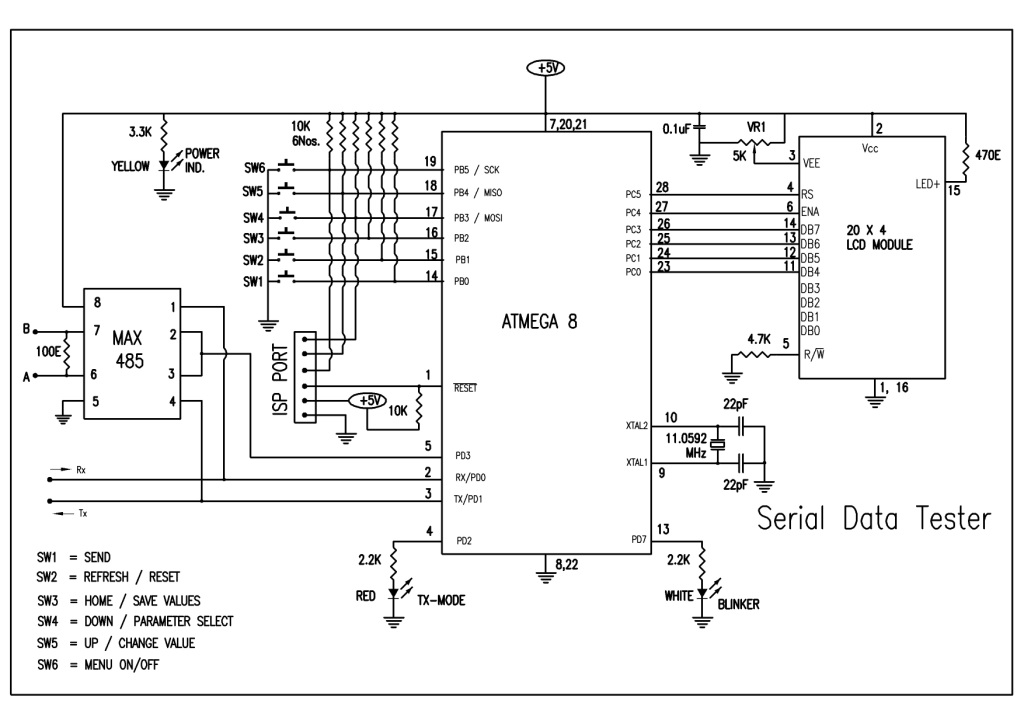
Schematics
Author
Hami Mahdavinataj
- 1 project
- 4 followers
Published on
November 30, 2018Members who respect this project
and 18 others
See similar projectsyou might like
Table of contents
| Serial Communication tutorial |
This tutorial focuses to teach you how to program AVR Serial Communication (UART). UART plays an important role in almost every embedded applications which we see in our day to life and hence it was considered to be very important concept in every Microcontroller.
The above design demonstrates the usage of UART to send and receive data via hyperterminal as well display the received data in 1 16×2 LCD. As we all know Microcontroller works in TTL logic which is not compatible with the PC so we have to employ a level converter IC MAX232, read more about the working of IC MAX232.
REGISTERS USED IN AVR SERIAL COMMUNICATION:
In AVR there are five registers which are meant to use for Serial Communication such as UDR, UBBR , UCSRA, UCSRB, UCSRC. Lets see the functions of these registers briefly.
UDR:
| UDR Register |
UDR or USART Data Register is meant for writing and receiving the data through the UART. In this there are two shift registers referred to as Transmit Shift register and Receive Shift register with each having a separate buffer register. When the data is written to UDR it will be transferred to Transmit Data buffer register and when we read the contents of the Receive Data buffer register is returned.
UBRR:
In AVR the baud rate of the UART is programmable and it is achieved by means of this UBRR register. It is 16 bit register classified into lower UBRRL and higher UBRRH out of which 12 bit is usable The formula governing the relation between the value of UBRR and Oscillator is
Baud Rate = (Oscillator Frequency / (16( UBRR Value +1))
So for a 8MHz oscillator frequency and 9600 baud rate the value need to be loaded in the UBRR will be
UBRR = (8MHZ /16(9600))-1
=(500KHz/ 9600) – 1
= 51 ( equivalent hex 33)
UCSRA:
| UCSRA Register |
UCSRB:
| UCSRB Register |
UCSRC Register:
| UCSRC Register |
STEPS TO PROGRAM UART:
- Load the hex value in the UBRR Register for the Baud rate you are about to use.
- Set the bits in the registers UCSRA, UCSRB & UCSRC based on your usage requirement.
- For Transmission Place the data in the UDR register and check for the appropriate flag to set in the UCSRA regsiter
- Clear the Flag for further transmission.
- For receiving the data, wait for the Receive flag to set in the UCSRA register and then read the UDR register to obtain the received data for processing or display.
- Clear the Flag for further data reception.
CODE:
JLCPCB - Only $2 for PCB Prototype (Any Color)
24 Hours fast turnaround, Excellent quality & Unbeatable prices
Up to $20 shipping discount on first order now: https://jlcpcb.com/quote